Author : MD TAREQ HASSAN | Updated : 2020/06/23
Model binding
- Model binding is a feature that maps incoming http data to model (poco)
- Retrieves data from various sources such as route data, form fields, and query strings
- Provides the data to controllers and Razor pages in method parameters and public properties
- Converts string data to .NET types
- Updates properties of complex types
- model binder is a feature of the framework that performs a lot of the heavy lifting behind the scenes
- Links:
Overview
Image courtesy: https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/introduction-to-asp-net-mvc-model-binding/
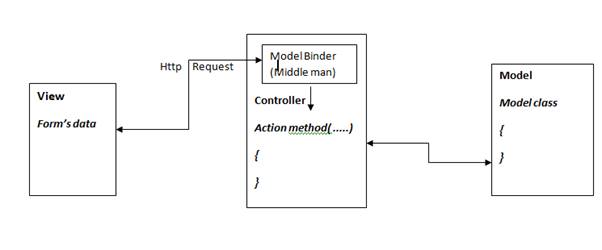
Binding types:
- Binding primitive data types: ModelBinder maps premitive types (i.e. int) to controller action (method) parameter(s)
- Binding complex data types: ModelBinder uses reflections to get the public properties and then binds to each of parameters in turn
Binding Source
By default, model binding gets data in the form of key-value pairs from the following sources in an HTTP request (sources are scanned in the order indicated in the list):
- Form fields
- The request body (API Controllers)
- Route data
- Query string parameters
- Uploaded files
- To implement custom source (i.e. cookies or session state): https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/models/model-binding#additional-sources
Binding targets
Model binding tries to find values for the following kinds of targets:
- Parameters of the controller action method that a request is routed to.
- Parameters of the Razor Pages handler method that a request is routed to.
- Public properties of a controller or PageModel class, if specified by attributes.
By default, a model state error isn’t created if no value is found for a model property. The property is set to null or a default value:
- Nullable simple types are set to null.
- Non-nullable value types are set to default(T). For example, a parameter int id is set to 0.
- For complex Types, model binding creates an instance by using the default constructor, without setting properties.
- Arrays are set to Array.Empty
(), except that byte[] arrays are set to null.
[BindRequired] attribute
- Use this attribute/annotation if model state should be invalidated when nothing is found in form fields for a model property
[BindRequired]behavior applies to model binding from posted form data, not to JSON or XML data in a request body- Request body data is handled by input formatters
Type conversion errors
If a source is found but can’t be converted into the target type, model state is flagged as invalid and:
- Web App controller: property is set to null or a default value
- API controller that has the
[ApiController]attribute: invalid model state results in an automatic HTTP 400 response - if you don’t want type conversion errors to result in model state errors: make the model property a string and perform the data conversion manually
Common binding annotations
- If target is ‘all properties of model’ then just using
Action(Foo fooModel)will work fine [Bind]:- Use bind when you need to perform special operations i.e. include of specific peoperties
- See: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45256439/when-to-use-bindattribute
- model binding of complex types (from incoming form data or JSON to POCO)
- Can be applied to a class or a method parameter
[BindRequired]:- Can only be applied to model properties, not to method parameters
- If binding cannot happen, this attribute adds a ModelState error
[BindNever]: Tells the model binder to ignore this parameter[FromHeader]: Forces binding from the HTTP request header[FromQuery]: Forces binding from the URL’s query string[FromRoute]: Forces binding from values provided by Routing[FromForm]: Forces binding from values in the FORM[FromBody]: Forces binding from values in the body of the HTTP request[FromServices]: Binds the parameter from services provided by dependency injection
Content negotiation
Disclaimer: the following explanation to make it easy to understand model binding (might not be accurate w.r.t.)
- Model binder will try to bind source data (incoming data) to target based on incoming
Content-Type: ... - If content type is not found (or model binder could not figure out content type) => fall backs to default based on controller:
- WebApp: form
- API: json
IActionResult Foo(Hover hover)- all properties of
Hoverwill be populated - if binding is missing in source => depending on the data annotation applied to properties:
- either model state will be invalid
- or properties will be null
- all properties of
IActionResult Foo([FromForm]Hover hover):- data source: form (enfocing source has to be form)
- if source is not form posted data => error (http status code 415, unsupported)
IActionResult Foo([FromBody]Hover hover):- data source: json (enfocing source has to be json => API controller)
- if source is not json => error (http status code 415, unsupported)
IActionResult Foo([Bind(“X,Y,Z”)]Hover hover): Hover has ‘n’ properties, but binder will bind onlyX,Y,Z
Data annotations
- Namespace: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.componentmodel.dataannotations
- Nuget:
- PMC:
Install-Package System.ComponentModel.Annotations - https://www.nuget.org/packages/System.ComponentModel.Annotations
- PMC:
- Data Annotations are used for Model Validation:
- Entity Framework Entity: properties of entity use data annotations to enforce contraints (so that only valid data is inserted into database)
- Form input models (WebApp, Desktop App, Xamarin.Forms): properties of input model are marked with data annotations to enforce contraints (so that only valid data is coming from user)
- Built-in attributes (Model Validation): https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/models/validation#built-in-attributes
Model Binding example
Following example is for AspNetCore MVC (WebApp)
HoverInputModel.cs
public class HoverInputModel
{
public int FirstName { get; set; }
public int LastName { get; set; }
public string FullName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
// will be null (because there will be no input field in the form for this prop)
public string Bar { get; set; }
}
HoverController.cs
public class HoverController : Controller
{
// ... ... ...
// GET: Hover/Create
public IActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
// POST: Hover/Create
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create([FromFrom]HoverInputModel hoverInputModel)
{
// check model state
// process data
}
// ... ... ...
}
Create.cshtml
@model ModelBindingAndFormValidation.Models.HoverInputModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create";
}
<h1>Create Hover Info</h1>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form asp-action="Create">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Id" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Id" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Id" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="FirstName" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="FirstName" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="FirstName" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="LastName" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="LastName" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="LastName" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="FullName" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="FullName" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="FullName" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Email" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Email" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Email" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-primary" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
When form is posted to server, form data will be bound to HoverInputModel.Props
Notes:
asp-foris special tag helper that does not require use ofModeli.e. we can useNameproperty directly instead ofModel.Name- for other tag helpers, you have to use
Model.Xxx
Model Validation
- Process of ensuring incoming data conforms to contraints of model properties
- Both model binding and model validation occur before the execution of a controller action or a Razor Pages handler method
- For web apps, it’s the app’s responsibility to inspect ModelState.IsValid and react appropriately
- Web API controllers don’t have to check ModelState.IsValid if they have the
[ApiController]attribute. In that case, an automatic HTTP 400 response containing error details is returned when model state is invalid - Model Validation Details:
HoverInputModel.cs
public class HoverInputModel
{
[Required]
[Display(Name = "First Name")]
[Range(5, 50)]
public int FirstName { get; set; }
[Required]
[Display(Name = "Last Name")]
[StringLength(50, MinimumLength = 5, ErrorMessage = "Last name must have at least 5 characters")]
public int LastName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "{0} is required")]
[StringLength(100, MinimumLength = 10, ErrorMessage = "Name must have at least 10 characters")]
[RegularExpression(@"^[a-zA-Z\s]+$", ErrorMessage = "Please, use letters in the name. Digits are not allowed.")]
[Display(Name = "Full Name")]
public string FullName { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "{0} is required")]
[StringLength(100, MinimumLength = 1, ErrorMessage = "The {0} must be at least {2} and at max {1} characters long.")]
public string Email { get; set; }
// will be null
public string Bar { get; set; }
}
HoverController.cs
public class HoverController : Controller
{
// ... ... ...
// GET: Hover/Create
public IActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
// POST: Hover/Create
// To protect from overposting attacks, enable the specific properties you want to bind to, for
// more details, see http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=317598.
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create([FromFrom]HoverInputModel hoverInputModel)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
// perform EF core task here i.e. _context.Add(hoverInputModel);await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
return View(hoverInputModel);
}
// ... ... ...
}
Excluding model property
[Bind(Exclude= "id")]would not work in AspNetCore- use
[Bind(include= ...)](mention all props you want to include, don’t mention what you want to exclude) [Bind]attribute does not work for the web api if you receive the model as json. Use:[JsonIgnore]- Links:
MVC
[Bind(nameof(FirstName), nameof(LastName), nameof(FullName))]
public class HoverInputModel
{
// data annotation here
public string FirstName { get; set; }
// data annotation here
public string LastName { get; set; }
// data annotation here
public string FullName { get; set; }
// ignored (value will be null)
public string Bar { get; set; }
}
// OR
public void SubmitData([Bind(include= ...)]HoverInputModel hoverModel)
{
//... ... ...
}
API
public class MyModel
{
[JsonIgnore]
public string Name { get; set; }
// ... ... ...
}
// Action:
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Student([FromBody]MyModel model)
Prefixed form element
Annotation: [Bind(Prefix= "Foo")]DataModel model
public void SubmitData([Bind(Prefix= "Address")]AddressModel addressOnly)
{
//even if id property was provided, model binder will ignore it
}
Custom validation attribute
See: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/models/validation#custom-attributes
Model Binding and Validation for Web API
- Model Binding Source: request body (json payload)
- When ModelState.IsValid evaluates to false in web API controllers using the [ApiController] attribute, an automatic HTTP 400 response containing issue details is returned. For more information, see Automatic HTTP 400 responses
Hover.cs
public class Hover
{
// properties with data annotations
}
HoverController.cs
[ApiController]
public class HoverController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult AddFoo([FromBody]Foo foo) // JSON -> POCO
{
// following code is unnecessary in web api because Model validation errors automatically trigger an HTTP 400 response
//if(!ModelState.Isvalid){
// return View(foo);
//}
// EF Core
_fooDbContext.Add(foo);
return Created(foo);
}
}